Wireless communication is a big part of the online space, and several architectures exist for this type of network. One of them is LoRa, which functions like WiFi but with long-range and low power consumption.
What is LoRa & LoRaWAN?
LoRa stands for Long Range, and it is a proprietary low-power, long-range wireless communication system. The wireless modulation technique derives its operational design on Chirp Spread Spectrum (CSS) technology, encoding data on radio waves using chirp pulses.
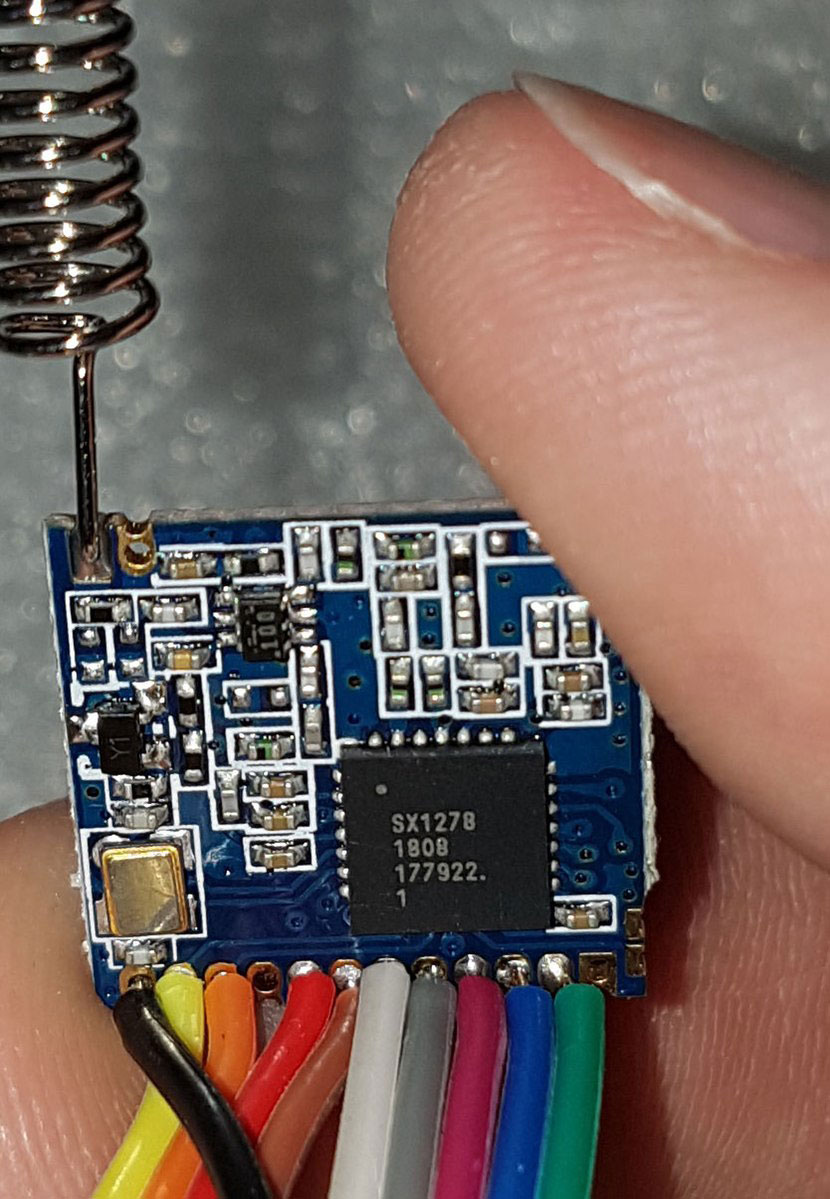
A LoRa module with an antenna
LoRa runs on a license-free wireless spectrum, like WiFi, but usually in the sub-gigahertz bands. However, you can operate it in 2.4 GHz because the exact frequency used with LoRa communication depends on the physical deployment location.
Some people use LoRa and LoRaWAN interchangeably, but the two are different. LoRa is the wireless communication hardware, while LoRaWAN is a Media Access Control (MAC) layer network protocol built for LoRa modulation. In simple terms, LoRaWAN is software that dictates how to use LoRa hardware.
What are LoRaWAN Gateways & Nodes?
LoRaWAN nodes and gateways are two of the four primary components in the LoRaWAN network architecture. Nodes (end nodes) are the edge sensors or devices in the network, while gateways gather data from several end nodes to send it to the network server and vice versa. The remaining two components are the network server and application server.
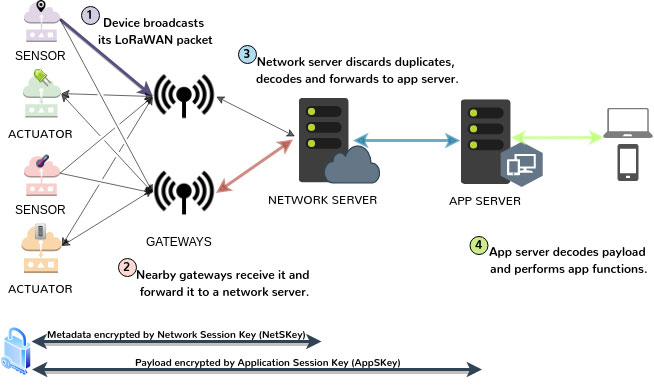
LoRa network architecture. Note the four components (end nodes, gateways, a network server, and an application server)
How Does A LoRa Gateway Work?
LoRa hardware operates on top of the LoRaWAN network protocol software, sending small, encoded data packets over a long range using chirp pulses (with a linear frequency variation). This network communicates with the end nodes back and forth.
In the US, the ISM frequency designated for LoRa technology is 915 MHz, and it has a 10-km transmission range with a line of sight. Therefore, in urban areas, expect a 3-km range max. But the network is reliable because a frequency offset between the transmitter and receiver reduces the bandwidth by around 20% without disrupting the decoding performance. This reliability helps minimize packet loss.
The gateway consists of the hardware and application software required to link the end nodes to the cloud. Since there are several gateways in the network, the one with the most stable link with the IoT device passes the packet to the server. The rest of the gateways are for redundancy in case one fails.
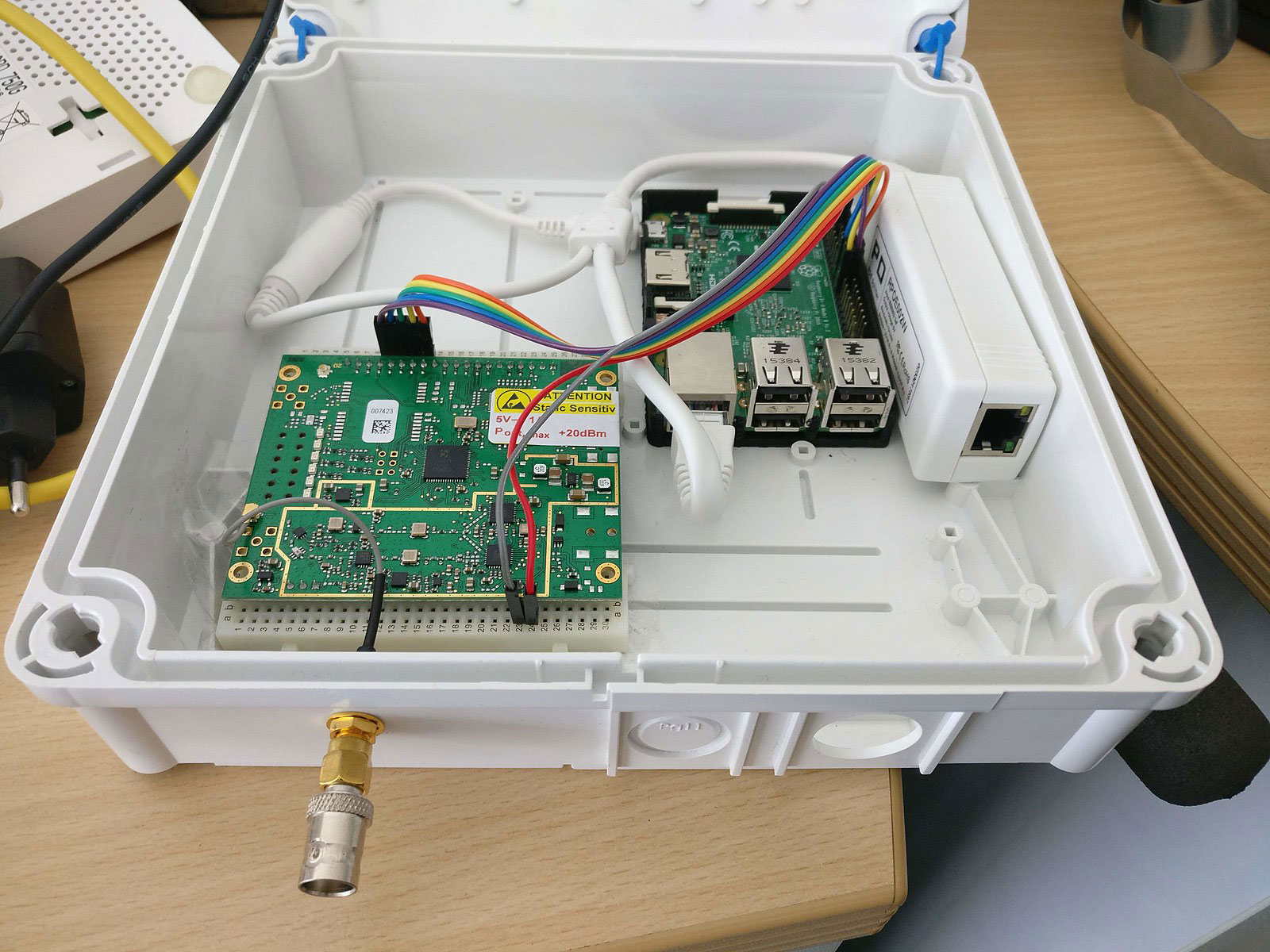

A LoRaWAN gateway
